The Corporate Transparency Act (CTA) is poised to revolutionize the U.S. business environment by enhancing transparency and accountability. Explore 10 frequently asked questions about the act and gain a better perspective of its implications.
Jump to ↓
| 1. What is the Corporate Transparency Act (CTA)? |
| 2. Why was the Corporate Transparency Act introduced? |
| 3. Who needs to file a Beneficial Ownership Information (BOI) report? |
| 4. What information must be provided by beneficial owners? |
| 5. What are the penalties for non-compliance? |
| 6. How does the CTA impact accounting professionals? |
| 7. What tools can accounting professionals use to stay compliant with the CTA? |
| 8. Who is considered a beneficial owner? |
| 9. What are the key deadlines for filing reports under the Corporate Transparency Act? |
| 10. What are the benefits of the CTA for small businesses? |
The Corporate Transparency Act (CTA) is poised to revolutionize the U.S. business environment by enhancing transparency and accountability. The CTA, which was passed in 2021 and became effective on January 1, 2024, is designed to reveal the actual ownership of companies operating in or accessing the American market.
This law addresses the pressing need to combat illicit activities like tax fraud and money laundering, often facilitated by anonymous shell companies. Let’s explore frequently asked questions, the key aspects of the CTA, its impact, and the benefits it offers to firms.
1. What is the Corporate Transparency Act (CTA)?
The Corporate Transparency Act (CTA) is a significant U.S. law enacted in 2021, aimed at enhancing transparency in business ownership. Its primary goal is to gather detailed information about the ownership of certain entities operating in or accessing the U.S. market. The law took effect on January 1, 2024.
2. Why was the Corporate Transparency Act introduced?
The CTA was introduced to address the misuse of shell companies by concealing the identities of illicit actors. It is designed to combat money laundering, tax evasion, and other illegal activities.
| “For too long, it has been far too easy for criminals, Russian oligarchs, and other bad actors to fund their illicit activity by hiding and moving money through anonymous shell companies and other corporate structures right here in the United States.”
– Acting FinCEN Directior, Himamauli Das |
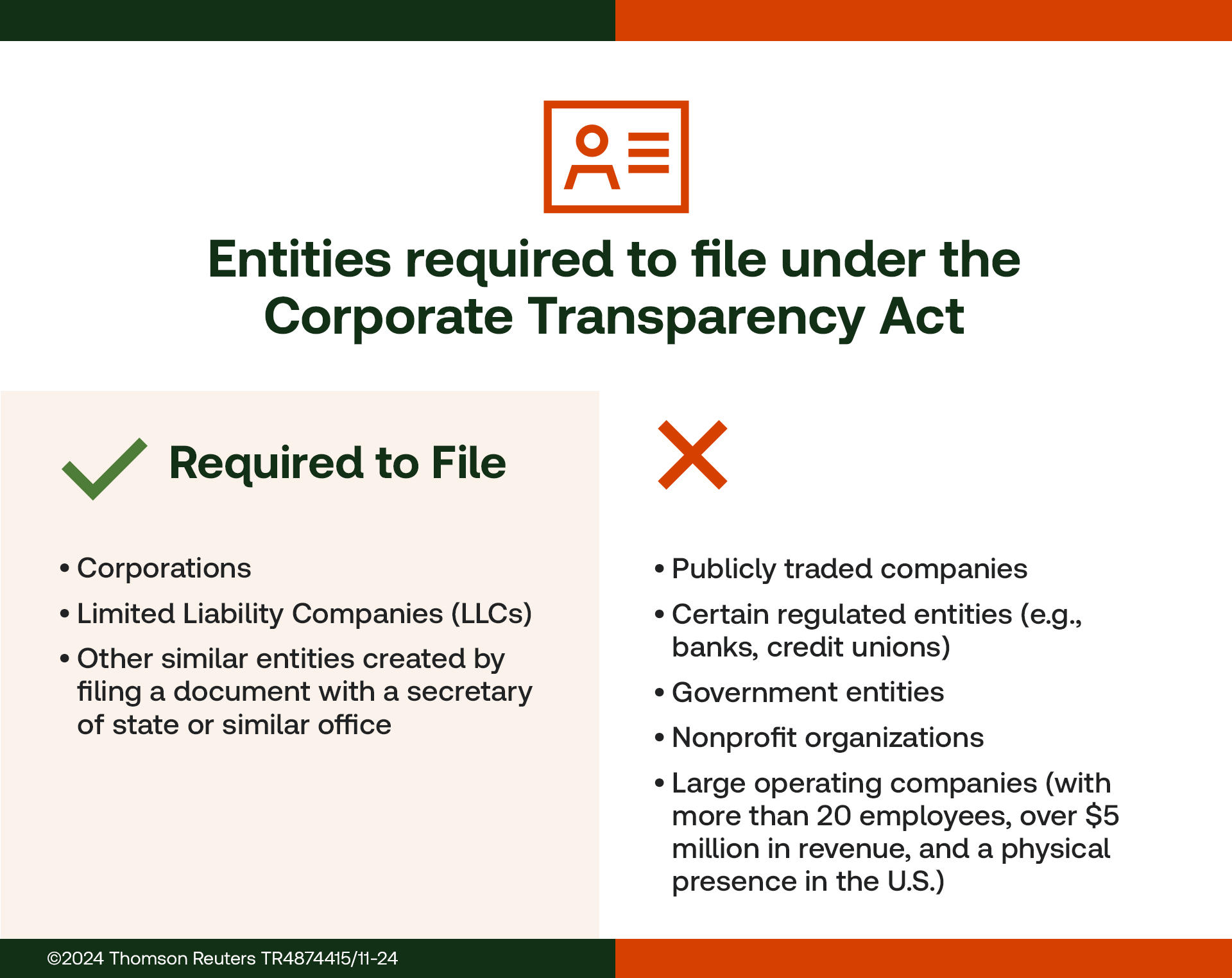
3. Who needs to file a Beneficial Ownership Information (BOI) report?
Entities required to file a Beneficial Ownership Information (BOI) report include:
- Domestic corporations
- LLCs
- Other entities are formed by filing documents with a state or tribal office
- Foreign entities registered to do business in the U.S.
It is important to keep in mind that there are exemptions for certain entities, such as banks, public accounting firms, and large operating companies.
4. What information must be provided by beneficial owners?
Beneficial owners must provide specific information, including their name, date of birth, address, and a unique identifier number from a recognized issuing jurisdiction. Additionally, a photo of the document, such as a passport or driver’s license, must be submitted.
5. What are the penalties for non-compliance?
Non-compliance with the Corporate Transparency Act can result in significant penalties, with fines ranging from $500 to $10,000 per violation and up to two years of imprisonment. These fines can accumulate, leading to substantial financial consequences for those who fail to comply.
6. How does the CTA impact accounting professionals?
For accounting professionals, the CTA presents an opportunity to expand their advisory services. However, it also increases administrative responsibilities related to due diligence and compliance monitoring. This expansion allows accounting professionals to explore new areas within their advisory services.
7. What tools can accounting professionals use to stay compliant with the CTA?
To maintain compliance with the CTA, accounting professionals should leverage comprehensive tax research platforms and solutions like CoCounsel Tax.
These advanced tools are essential for staying abreast of the latest regulatory changes and updates in the tax landscape. By utilizing these resources, professionals can access real-time information, in-depth analysis, and expert insights, enabling them to provide accurate and timely advice to their clients.
8. Who is considered a beneficial owner?
A beneficial owner is defined as any individual who exercises substantial control over a reporting company or owns or controls at least 25% of the ownership interests. There are five exemptions, including minors and employees acting solely in their capacity as employees.
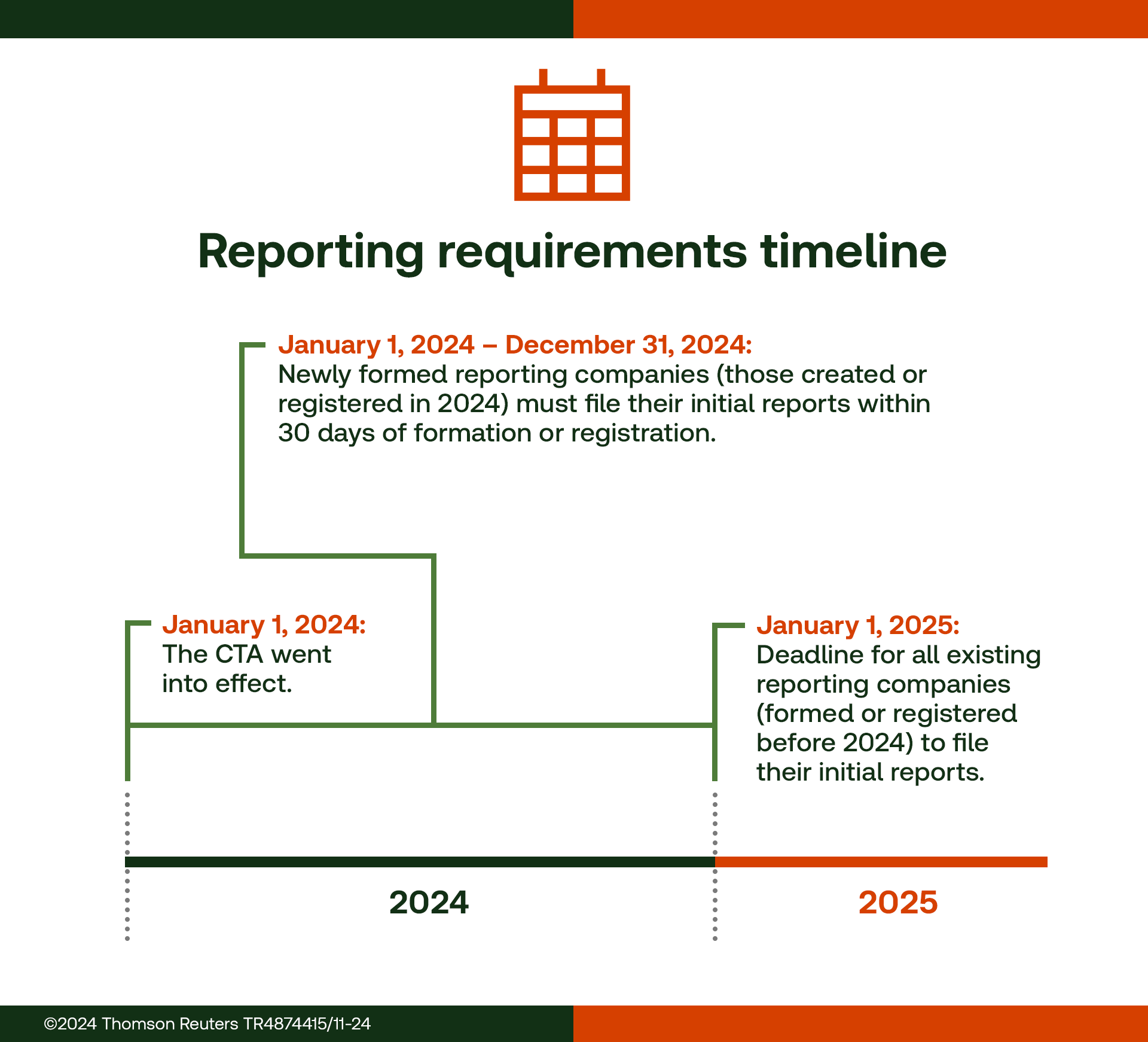
9. What are the key deadlines for filing reports under the Corporate Transparency Act?
The CTA outlines key deadlines for filing reports, with the effective date being January 1, 2024. Existing companies must submit initial reports by January 1, 2025, while new companies are required to file reports within 30 days of their creation or registration.
10. What are the benefits of the CTA for small businesses?
The CTA offers several benefits for small businesses, primarily by improving transparency in business activities. This enhanced transparency not only benefits the government and the economy but also helps level the playing field for smaller firms, fostering a fairer competitive environment.
Looking ahead: Understanding the impact of the Corporate Transparency Act
The Corporate Transparency Act is a pivotal step towards a more accountable and transparent business environment in the U.S. By mandating detailed ownership information, the CTA seeks to deter illicit activities and foster a fairer marketplace. For small businesses and accounting professionals, navigating this legislation presents both challenges and opportunities, ultimately contributing to a more transparent and competitive economic landscape.
 |
|