Jump to:
| The current state of GenAI training |
| The future of GenAI training |
| 5 ways tax professionals should prepare for expectations |
| What to look for in an AI assistant |
 |
2024 GenAI in Professional ServicesDiscover perceptions, usage, and impact on the future of work
|
As generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) continues to evolve, its impact on the tax profession is becoming increasingly significant. The professionals surveyed in the Thomson Reuters Institute’s 2024 Generative AI in Professional Services report demonstrated while adoption isn’t yet widespread, more than half of professionals believe they should use GenAI in their daily work — and they’re already planning for the specialized tools that will create this reality.
The integration of GenAI into tax-related tasks promises to revolutionize the industry by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. Take a look at the current state of GenAI training, the emergence of new job titles and companies influencing the future of GenAI, and how tax professionals should prepare for future expectations.
The current state of GenAI training
GenAI training is essential as it equips professionals with the knowledge and skills to leverage the technology effectively, ensuring they can maximize its potential benefits while mitigating associated risks. Despite the potential benefits of GenAI, the current state of training in this technology within the tax profession is underwhelming. According to the Thomson Reuters Institute’s 2024 report on GenAI in professional services, only 12% of respondents from the tax industry reported that their organizations provide GenAI training. This figure is significantly lower compared to other sectors such as corporate risk and fraud departments, where 38% of respondents indicated they received GenAI training.
Several factors contribute to this lack of training:
- Investment constraints: Training employees in new technologies like GenAI requires substantial resources, including time, money, and expertise. Many tax firms may prioritize other areas of investment, especially if they are still evaluating the return on investment (ROI) of GenAI.
- Caution and hesitance: There is a prevalent sense of caution and hesitance surrounding GenAI adoption in the tax industry. Concerns about the technology’s accuracy, data security, and potential over-reliance on AI contribute to this hesitance. As a result, firms may be reluctant to invest in training until they are more confident in the technology’s reliability and benefits.
- Rapid technological advancements: The fast-paced evolution of GenAI technologies can make it difficult for training programs to keep up. Organizations may struggle to develop training materials that remain relevant as new advancements and updates are continually introduced. There is a shortage of professionals with the expertise to train others in GenAI. This gap makes it challenging for tax firms to develop and implement comprehensive training programs.
The future of GenAI training
Technology companies are anticipated to be the primary influencers of the future of GenAI. According to the report, 83% of tax respondents identified technology companies as the top influencers, followed by corporations (46%) and government regulators (34%). These entities will play a pivotal role in shaping the development, adoption, and regulation of GenAI technologies.
As GenAI becomes more popular and more integrated into the tax profession with 31% of tax respondents stating that they expect new titles or job expectations within the next 3-5 years.
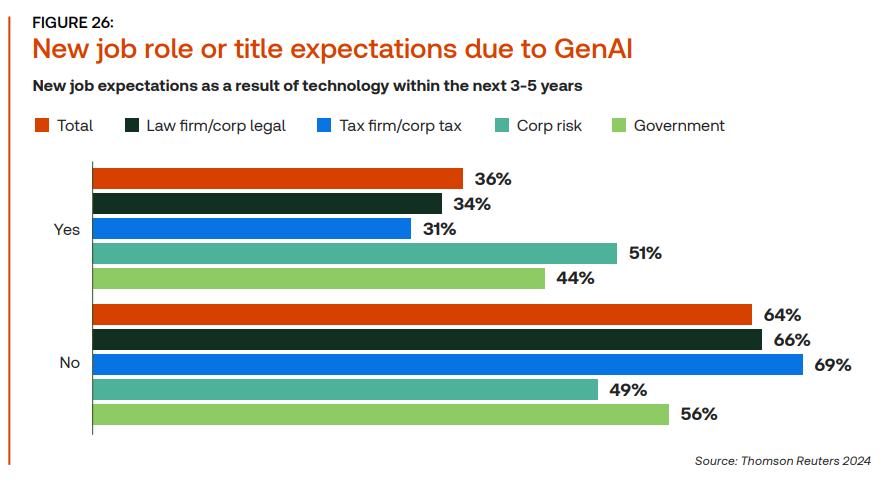
The report identifies several potential new job titles:
- AI Specialist: These professionals will focus on developing, implementing, and maintaining AI systems within organizations. They will ensure that AI tools are used effectively and ethically.
- Data Analyst/Expert: These roles will involve analyzing data generated by AI systems to provide insights and inform decision-making processes.
- Technology Consultant/Specialist: These roles will involve advising organizations on the best AI tools and practices to adopt, helping them navigate the complexities of AI technology.
These roles will be crucial in implementing, managing, and optimizing GenAI technologies within tax firms.
CoCounsel: The GenAI for professionalsTrained by industry experts, ours is the only GenAI assistant built on 150 years of authoritative content
|
|
5 ways tax professionals should prepare for expectations
Rather than viewing GenAI as a replacement for human expertise, professionals should consider it a complementary tool that can enhance decision-making and productivity. Strategic implementation of GenAI can lead to more efficient processes and improved outcomes in complex tasks. To navigate this landscape successfully, professionals need to focus on several key areas.
Invest in training
Tax professionals must prioritize GenAI training to stay competitive in the evolving landscape. Firms should invest in comprehensive training programs that cover the basics of GenAI, its applications in tax work, and best practices for ethical and responsible use. By equipping their staff with the necessary skills and knowledge, tax firms can ensure they are well-prepared to leverage GenAI effectively.
Embrace a proactive approach
Tax professionals should adopt a proactive approach to GenAI adoption. This involves staying informed about the latest advancements in GenAI and actively seeking opportunities to integrate these technologies into their workflows. By doing so, tax professionals and organizations can enhance their efficiency and provide higher-quality services to their clients.
Amplify professional expertise
GenAI can automate routine and repetitive tasks, allowing tax professionals to focus on work that amplifies their expertise. By leveraging GenAI for tasks such as tax return preparation, bookkeeping, and tax research, professionals can allocate more time to strategic decision-making and client advisory services.
Prioritize data security
Given the concerns about data security and privacy, tax professionals must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information. This includes developing protocols for secure data handling and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. By prioritizing data security, tax firms can mitigate risks and build trust with their clients.
Stay updated on compliance
As GenAI becomes more prevalent, tax regulations may evolve to address new challenges and opportunities. Tax professionals should stay informed about these changes to ensure compliance and provide accurate advice to clients. By keeping abreast of regulatory developments, tax firms can navigate the evolving landscape and avoid potential legal pitfalls.
What to look for in an AI assistant
The future of work in the era of GenAI presents both opportunities and challenges for tax professionals. By investing in training, adopting a proactive approach, and focusing on high-value tasks, tax professionals can effectively prepare for the transformative impact of GenAI. Tax professionals who embrace GenAI and its potential will be well-positioned to thrive in the future of work. By leveraging the power of GenAI, tax firms can enhance their efficiency, accuracy, and productivity, ultimately providing better services to their clients and staying ahead in a competitive industry.
In determining the most beneficial GenAI tool, professionals will want to ensure that the AI assistant’s developer has experience in or at least demonstrable knowledge of the professional’s field. A truly valuable AI assistant should access reliable information when the professional’s needs involve trends, data, and other types of research.
An AI assistant, and the company providing it, should also be able to prove that the tool will become even more helpful, accurate, and efficient in the future, evolving as one’s profession evolves. A question any professional should ask should be, will this tool help me uncover insights and meet challenges for situations that have yet to arise?
Public vs private AI
All this noted, there is a distinction between public AI and private AI. The main difference is that public AI scrapes the entire internet for research and data. As a result, a public GenAI tool may inadvertently access and make use of false information, private data, or material under copyright—major risks for any profession. By contrast, private AI uses “proprietary” databases that have been developed to access specific and trusted sources of data and research.
Choosing the right solution
Not all AI tools are created equal. Tax and audit professionals must conduct thorough research to minimize their exposure to potential tax and accounting AI risks. With Thomson Reuters’ CoCounsel, tax and accounting professionals can do just that and more.
- Improve the speed of the research phase by finding the summarized answers you need quickly.
- Increase confidence in AI-assisted answers with links to relevant editorial content and source materials from a broad collection of data sets and expert knowledge of Checkpoint Edge.
- Enable senior staff to redirect their efforts toward higher-value work while junior staff learn and develop good question techniques with AI-assisted research.
This tax-specific private GenAI assistant can perform sophisticated research and analyze dense, voluminous information — and then deliver reliable, accurate, and thorough answers as quickly as you need them. It has been trained by industry experts to handle essential but repetitive tasks so that professionals can focus on more profitable uses of their time. With the latest technology, you should be able to clarify the complex.
 |
2024 GenAI in Professional ServicesDiscover perceptions, usage, and impact on the future of work
|










