The indirect tax landscape is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the relentless pursuit of efficiency, accuracy, and strategic advantage. A recent Thomson Reuters webinar underscored the critical role of technology and automation in reshaping the indirect tax department. This blog looks at the key challenges faced by tax professionals and explores the emerging technological solutions that are poised to revolutionize the function.
Jump to ↓
| The imperative for change |
| The rise of AI in indirect tax departments |
| Upskilling the workforce for a tech-enabled future |
| A tech and AI-driven future for indirect tax |
The imperative for change
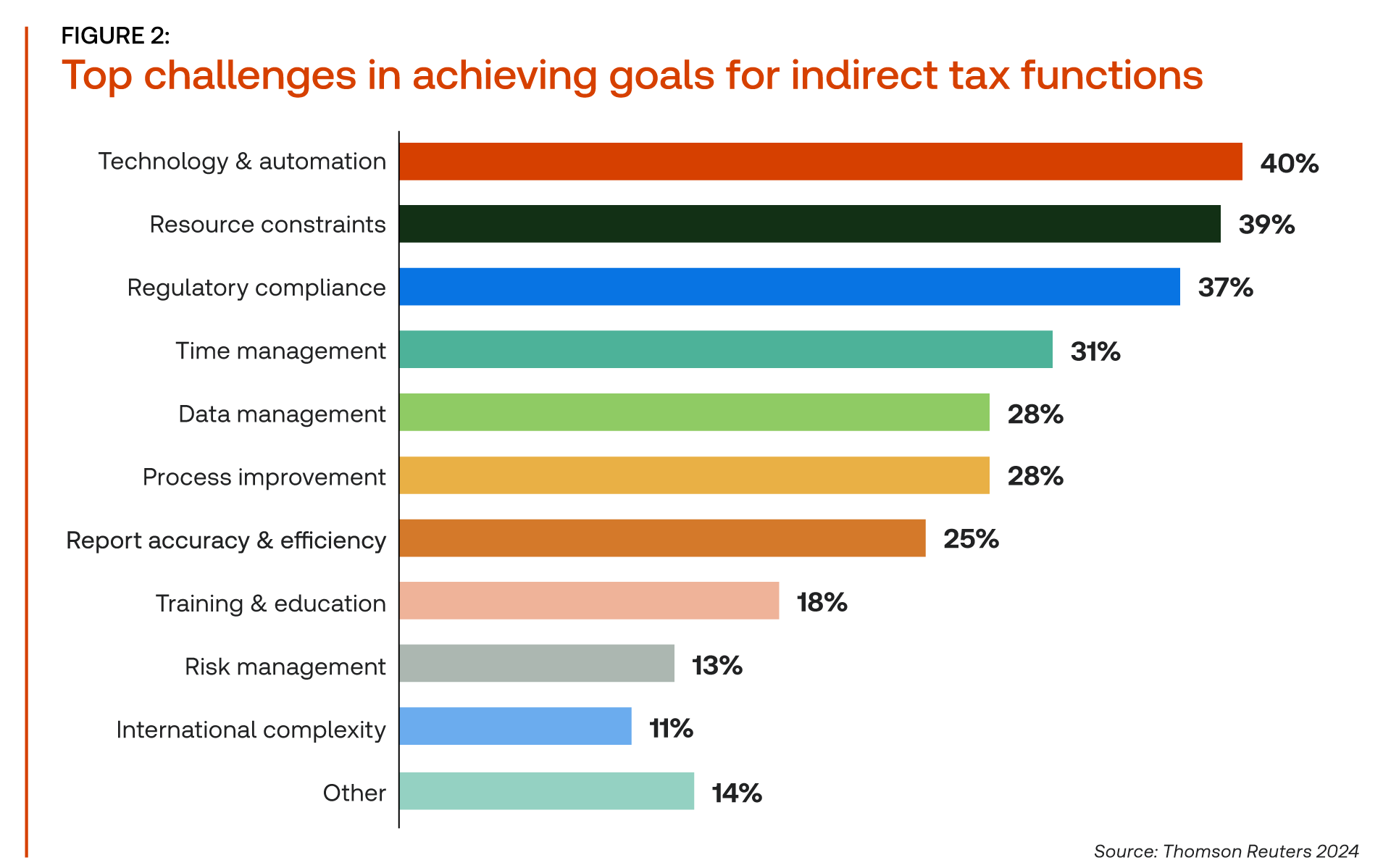
The indirect tax function is under immense pressure to deliver on multiple fronts. A recent Thomson Reuters Institute report revealed that 37% of tax professionals cite increasing regulatory complexity as a top challenge. Concurrently, 39% reported resource constraints as a significant hurdle. These pressures have underscored the urgent need for transformation.
The webinar emphasized that success hinges on achieving both accuracy and efficiency. As Nadya Britton, Enterprise Content Manager – Tax and Accounting at the Thomson Reuters Institute, stated, “Success for the indirect tax department is about accuracy and efficiency.” However, the path to this ideal state is obstructed by several challenges:
- Technology and automation lag: A significant proportion of indirect tax operations still rely heavily on manual processes, leading to inefficiencies, errors, and increased compliance risks.
- Resource constraints: Limited staff and budget allocations hinder departments from keeping pace with the dynamic regulatory environment.
- Increased regulatory complexity: The intricate web of indirect tax regulations, varying and constant changes across jurisdictions, demands consistent attention and expertise.
The rise of AI in indirect tax departments
The good news is that technology offers a powerful antidote to these challenges. The webinar highlighted the transformative potential of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation. AI-powered solutions can automate a wide range of time-consuming tasks, including:
- Data extraction and analysis: indirect tax technology solutions can efficiently extract relevant data from various sources, reducing manual effort and improving data
- Indirect tax management: Content-driven tax technology solutions can automate sales tax calculations, returns and audits, minimizing errors and streamlining compliance
- Compliance risk assessment: AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify potential compliance risks enabling proactive mitigation strategies
- Fraud detection: AI algorithms can detect anomalies and patterns indicative of fraudulent activities, safeguarding revenue
Christian Jensen, Director, Technology Vertical at Thomson Reuters, emphasized the transformative power of AI, stating, “We see AI being leveraged to go in and scrape that data and look at and identify those anomalies.”
Upskilling the workforce for a tech-enabled future
While technology promises to revolutionize the indirect tax function, human expertise remains indispensable. The webinar stressed the importance of upskilling the workforce to effectively leverage new technologies. A significant majority of companies (78%) surveyed to invest in employee training to bridge the digital skills gap.
Upskilling will equip tax professionals with the ability to collaborate with AI and automation tools, enabling them to focus on higher-value strategic tasks such as tax planning, risk management, and business advisory.
The evolving role of tax technologists
The convergence of tax expertise and technology has created a relatively new role: the tax technologist. These professionals possess a unique blend of skills, enabling them to bridge the gap between the tax technical and tax technology. Tax technologists will play a pivotal role in driving digital transformation and ensuring the successful implementation of tax technology solutions.
A tech and AI-driven future for indirect tax
The future of the indirect tax department is undoubtedly tech-driven. By embracing AI, automation, and upskilling initiatives, indirect tax professionals can create a more efficient, accurate, and strategic function. This transformation will not only streamline operations but also empower tax teams to contribute more meaningfully to overall business objectives.
To fully realize the potential of technology, tax departments must adopt a holistic approach that encompasses:
- Strategic vision: Developing a clear technology roadmap aligned with business goals.
- Data management: Establishing robust data governance and management practices.
- Talent development: Investing in employee training and upskilling programs.
- Change management: Effectively communicating the benefits of technology and managing resistance to change.
Each of these are a separate workstream which can be planned and delivered by the tax team as a part of adopting a more technology driven approach.
By embracing these principles, tax departments can position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly complex and competitive environment.
 |
|
 |
|